An introduction to the python shell either in IDLE or https://repl.it/
- Run IDLE or in the repl.it window
- Assigning a value to a variable
- Using the python shell as a calculator
- Printing a word
- Printing a number
- Printing the content of a variable
- Comparing two numbers
- comparing two variables
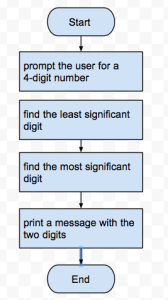
Writing your first python program:
- If you are using IDLE, create “My_Python_Programs” folder in Documents”
- If you are using IDLE or repl.it, create a new “Basic_Progrmas” folder in the “My_Python_Programs”
- Open a “new window”
- Write your first program using the algorithm to find the smallest and largest numbers in a set of 2 integer numbers. Program name: BasicInstructions_YI.py.
NOTE: YI_ represents Your Initials.
Guidelines for writing programs
Every program has to have a header:
- Assignment description
- Author’s name
- Date
- Input and output as comments if they are part of the assignment
- If the program doesn’t run successfully, write a short paragraph as part of the program header explaining the problem.
Set of instructions:
- Comparing two numbers
- Deciding which number smaller and which one is larger
Let’s turn the English instructions into computer instructions:
###################################################################
# Mrs. Elia
# python 3.x
# Description: Basic instructions
###################################################################
name = input("Enter your name ") # prompting the user
print("Hello", name) # displaying a message
x = input("Enter a number ") # Assignment operator
print ("The first number you entered is ",x ) # Why green and black?
y = input("Enter another number ") # prompting for another number
print ("The two numbers you entered are",x,"and", y) # printing multiple items
# Anything inside quotes is a "string" or text
###################################################################
#
# Turn the "string" numbers into "integer" numbers to compare them
#
###################################################################
x = int(x) # convert to string and assign
y = int(y) # convert to string and assign
if x > y: # compare x to y
print (x, " is bigger than ",y) # the comparison is true
else:
print (y, " is bigger than ",x) # the comparison is false
# end of program
What about if they are both equal to each other?
if x == y:
print("They are both equal")
else:
if x > y:
print (x, " is bigger than ",y)
else:
print (y, " is bigger than ",x)
Concepts you learned
1. Variables as place holders
2. Keeping an eye on only two variables at a time
More concepts to learn
3. Pseudocode
4. Flowchart
More on “ordering”
Install python and IDLE in your home computer videos or work on repl.it:
Write English instructions (pseudocode) to order 3 numbers from small to large.
Use the following data to “trace” your algorithm.
89 101 2
Explain your strategy in a short paragraph.
Videos From the “Resources Tab” above:
Python programming using repl.it
Python Programming using IDLE
Creating a file in repl.it
Creating python file in IDLE
Introduction to Python and IDLE
Some help on running python programs in mac os x
Some help from Al Sweigart’s video using pc.